F x g x y 1 y 2 x 2 x x 1 x ² x x 1 x ² 1bf x g x y 1 y2 x 2 x x 1 x ² x x 1 x from COLLEGE OF 123 at Nueva Ecija University of Science and TechnologyF(x) = (x1)(x2)(x3) , x ∈0,4, ∴ f(x) = x 3 6x 2 11x 6 As f(x) is a polynomial in x (1) f(x) is continuous on 0, 4 (2) f(x) is differentiable on (0, 4) Thus, all the conditions of LMVT are satisfied To verify LMVT we have to find c ∈ (0,4) such that `"f'" ("c") = ("f"(4 )"f"(0))/(40)` (1) Now `"f"(4) = (41)(42)(43) = 6` f(0) = (01)(02)(03) = 6 andGiven f (x) = 3x 2 – x 4, find the simplified form of the following expression, and evaluate at h = 0 This isn't really a functionsoperations question, but something like this often arises in the functionsoperations context
F X X 2 2x 4 X 2 F X X 2 4x X 2 2 F X 8 X 2 3 How To Find The Domain Of F X X And Y Intercepts Vertical Asymptotes The Critical Numbers Concave Up And Down And Sketch Graph Socratic
F x x 1/x 2 2x-1
F x x 1/x 2 2x-1-Assume f ( x 1) = f ( x 2) Then x 1 2 1 = f ( f ( x 1)) = f ( f ( x 2)) = x 2 2 1 and so x 2 = ± x 1 Then from f ( f ( − x)) = f ( f ( x)) we conclude that f ( − x) = ± f ( x) for all x Define g 0, ∞) → 0, ∞) by g ( x) = f ( x) For x with g ( x) = f ( x) we haveIt follows that f x (t) = e tx for every t in R Lie algebras



Biomath Functions
Free PreAlgebra, Algebra, Trigonometry, Calculus, Geometry, Statistics and Chemistry calculators stepbystep Example 10 Show that the function f N N, given by f (1) = f (2) = 1 and f (x) = x 1, for every x > 2, is onto but not oneone Here, f(x) = 1 for =1 1 for =2 1 for >2 Here, f (1) = 1 f (2) = 1 Check onto f N N f(x) = 1 for =1 1 for =2 1 for >2 Let f(x) = y , such that y N Here, y is a natural number & for every y, there is a value of xThe maximum occurs where the denominator x^2 2 is at a mininum Clearly, x^2 2 must have a minimum of 2, because x^2 is either 0 or positive So the maximum value of f(x) is 1/2, and occurs at x = 0 On the other hand, there is no minimum, bec
X_0 = 0 y = (x^2 3x 1)(2 x);Starts with f0=1/2 and f=x1/2 Looking at this picture it is evident that the derivative goes through some jumps I suspect it is possible to show that there are no solutions which are differentiable everywhere because the way the derivative changes betweens iterations depends on x and the sided derivatives will not always agreeX2 ··1 n!
Domain of f (x) = x/ (x^21) WolframAlpha Area of a circle?X_0 = 1 y = x 7/5 2x; f' (x) = 1/ (1x^2)^2 d/dx (1)d/dx (x^2) The derivative of 1 is zero f' (x) = (d/dx (x^2)0)/ (1x^2)^2 Simplify the expression f' (x) = (d/dx (x^2))/ (1x^2)^2 Use the power rule, d/dx (x^n) = n x^ (n1), where n = 2 d/dx (x^2) = 2 x f' (x) = 1/ (1x^2)^2 2 x



Find The Limit As X Goes To 0 Of Arcsin X X 1 X2 Stumbling Robot
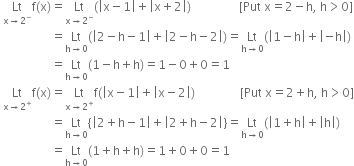



Discuss Continuity Of The Function F Given By F X X 1 X 2 At X 1 And X 2 From Mathematics Continuity And Differentiability Class 12 Cbse
1) f(x) 2 A) (x)8 2) 3f(x) B) 1 3 x 8 3) f(x) C) x8 ( 2 4) f(x 2) D) x8 2 5) 1 3 f(x) E) (x 3) 8 6) f(3x) F) x8 7) f(x) 2 G) (x 2)8 8) f(x) H) (3x)8 9) f(x 2) I) 3x8 10) f(x 3) J) (x 2)8 For #11 and #12, suppose g(x) = 1 x Match each of the numbered functions on the left with the lettered function on the rightSimple and best practice solution for F(x)=x^23x1 equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework If it's not what You are looking for type in the equation solver your own equation and let us solve itX_0 = 1 y = x/2x 3;



Functions And Linear Equations Algebra 2 How To Graph Functions And Linear Equations Mathplanet




If F X 2x 1 If X Gt 1 And X 2 1 If 1 Lt X Lt 1 And If F 1 F 3 F X F 2 F Youtube
Get an answer for '`f(x) = x/(x^2 1)` (a) Find the intervals on which `f` is increasing or decreasing (b) Find the local maximum and minimum values of `f` (c) Find the intervals of concavityHere we have the function f(x) = 2x3, written as a flow diagram The Inverse Function goes the other way So the inverse of 2x3 is (y3)/2 The inverse is usually shown by putting a little "1" after the function name, like this f1 (y) We say "f inverse of y" So, the inverse of f(x) = 2x3 is written f1 (y) = (y3)/2 Ex 51, 34 Find all the points of discontinuity of f defined by 𝑓(𝑥)= 𝑥 – 𝑥1Given 𝑓(𝑥)= 𝑥 – 𝑥1 Here, we have 2 critical points x = 0 and x 1 = 0 ie x = 0, and x = −1 So, our intervals will be When 𝒙≤−𝟏 When −𝟏




F X X2 2x 1 G X 7x 5 F X X4 2x2 Chegg Com




For Which Of The Following Functions F Is F X F 1 X For All X Gmat Tutor In Nyc Online
That tells us that F of X is going to be equal to negative the anti derivative of one over X is actually going to be the natural log of the absolute value of X So then based on that, what we end up having is um plus C X Class D Um And the reason why we have plus six is because this is some constant So it's anti derivative of B plus C XEasy as pi (e) Unlock StepbyStep Natural Language Math Input NEW Use textbook math notation to enter your math Try it ×Divide f2, the coefficient of the x term, by 2 to get \frac{f}{2}1 Then add the square of \frac{f}{2}1 to both sides of the equation This step makes the left hand side of



Biomath Functions




F R Gt R F X X 1 X 2 Determine Intervals In Which The Given Function Are Strictly Increasing Or Brainly In
Piece of cake Unlock StepbyStep Natural Language f x = x 2 g x, g 1 = 6 a n d g ' 1 = 3 ⇒ f ' x = 2 x g x x 2 g ' x ⇒ f ' 1 = 2 1 g 1 1 2 g ' 1 ⇒ f ' 1 = 2 1 6 1 3 = 12 3 = 15 ⇒ f ' 1 = 15 Hope this information will clear your doubts about topic If you have more doubts just ask here on the forum and our experts will try to help you out as soon as possible RegardsLet F (X) =`{ (1 X, 0≤ X ≤ 2) , (3 x , 2 < X ≤ 3)}` Find Fof




Solution If F X 1 1 X 2 Then What Is F X
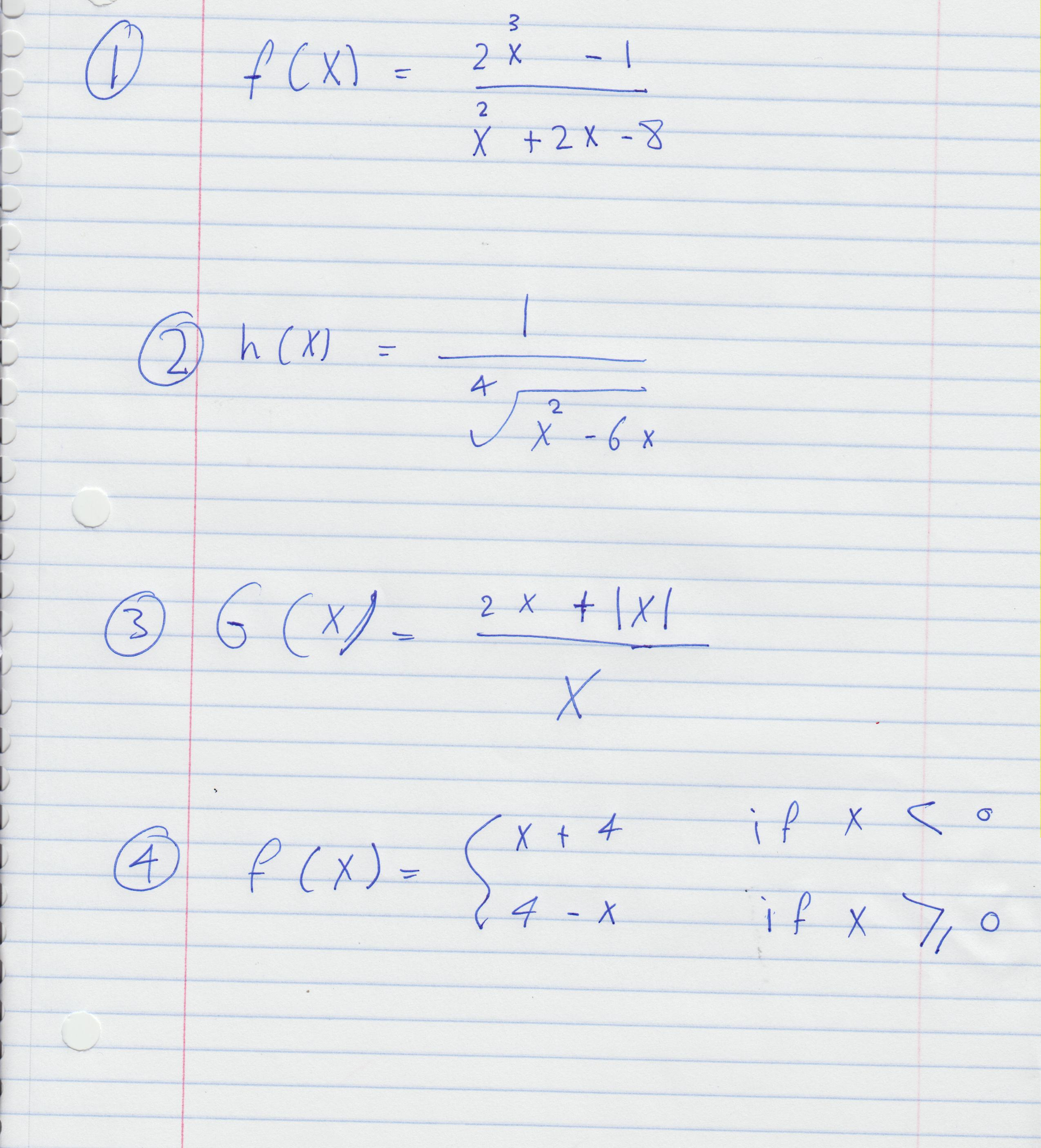



F X 2x3 1 X2 2x 8 H X 1 6 X 2x Chegg Com
Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ If f(x) = x√(1 x^2) then fofof(x) = Examine the differentiability of f, where f is defined by f(x) = {x2 sin1/x, if ≠ 0 , at x = 0, if x = 0 asked in Class XII Maths by nikita74 (E˘ xn1 for some ξ strictly between 0 and x • (c) For n = 1, we get ex = 1x 1 2 e˘x2 Since e˘ > 0, it follows that ex ≥ 1 x, with equality if and only if x = 0 • (d) Take x = π e −1 in the inequality from



Secure Media Collegeboard Org Digitalservices Pdf Ap Apcentral Ap15 Calculus Q5 Pdf



What Is The Inverse Of The Function F X X X 1 Quora
X_0 = 0 y = (3 Squareroot x x)(2 x^2); $f(x) = \frac{x 1}{x 2}$ could represent the set of pairs (1, 0) (0, 1/2) (1, 2/3) But it could also represent the set of pairs (0, 1/2) (1, 2/3) (2, 3/4) Both of these are two completely different functions Morale a formula like $f(x) = \frac{x 1}{x 2}$ is not a functionGraph f(x)=(x^21)/(x1) Rewrite the function as an equation Use the slopeintercept form to find the slope and yintercept Tap for more steps The slopeintercept form is , where is the slope and is the yintercept Find the values of and using the form
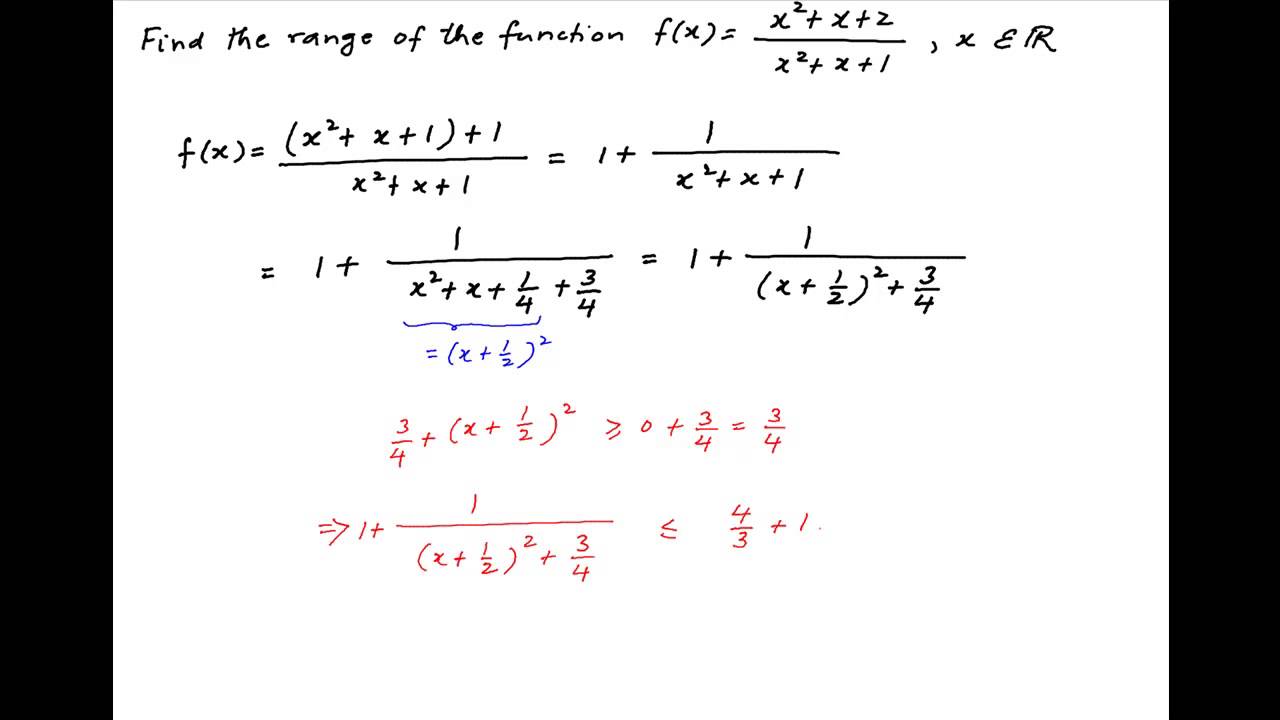



Find The Range Of F X Square X X 2 Square X X 1 Youtube



Solution Find The Inverse Of F X 2 X 1
F(x) = 1/x, g(x) = 1/xG(x) = x² x 1 = (x − ω)(x ω²), where ω = (−1 i√3)/2 is cube roots of unity For cube roots of unity ω, we have, two important properties;F(x) = x 2 1 = 0;




Alex S Work For Finding The Inverse Function For F X 2 3 X 1 An Download Scientific Diagram
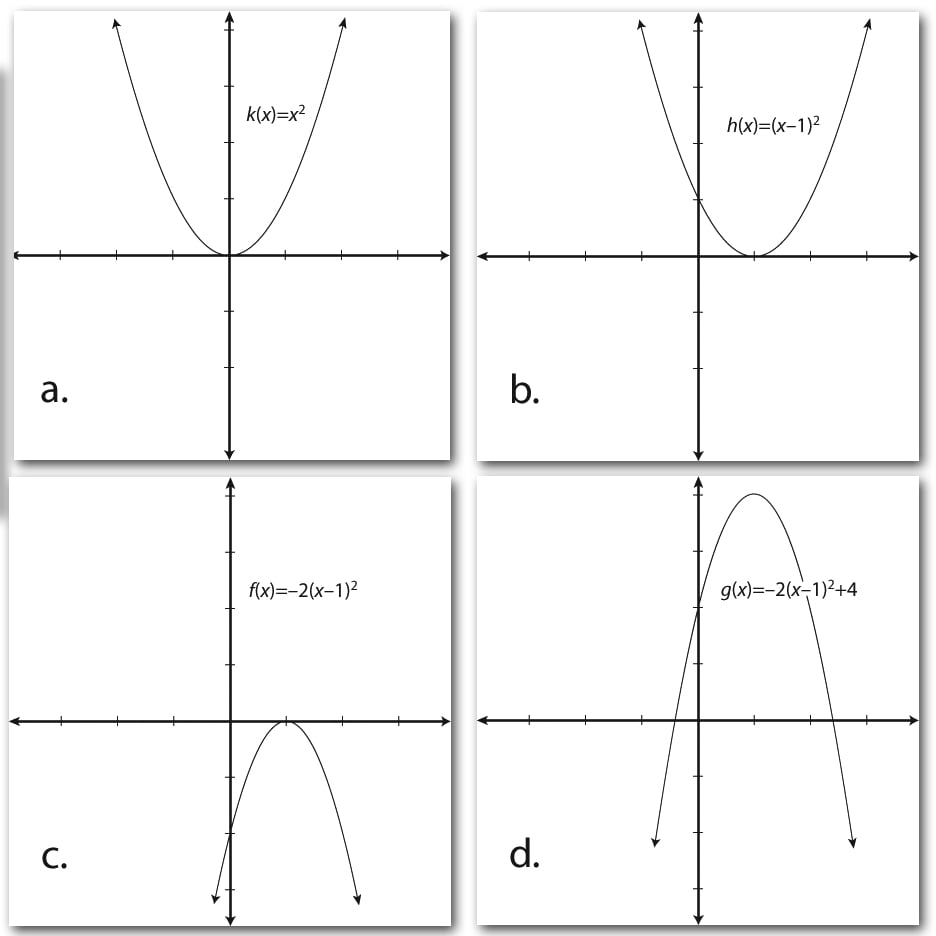



How To Combine Various Transformations Dummies
Please Subscribe here, thank you!!!Free functions calculator explore function domain, range, intercepts, extreme points and asymptotes stepbystep Let f = {(x, x 2 /(1 x 2)) x ∈ R} be a function from R to R Determine the range of f



What Is The Minimum Value Of F X X 1 X 2 X 3 Quora




Let F X X 2 1 X 1 X 2 2 X 2 X 3 Chegg Com
Video Transcript So in this problem we are asked to find f prime at a when half of x is X to the 2 Well, by definition, if private A Is the limit as H approaches zero of F Of a plus H minus F of a over H All right So that means that this is now the limit as h approaches zero F of a plus age and in this function F of XF (x_1, x_2) = 2x_1 3x_2 WolframAlpha Volume of a cylinder?Now, that last example is not to be said it can't be done, but it involves completing the square to obtain f(x) = (x2) 2 2, then inversing it so that you get f1 (x) = 2sqrt(x2) However, there is another way that doesn't rely so much on informality and will work whether or not you can figure out exactly what you did with exactly one x




Improper Integrals
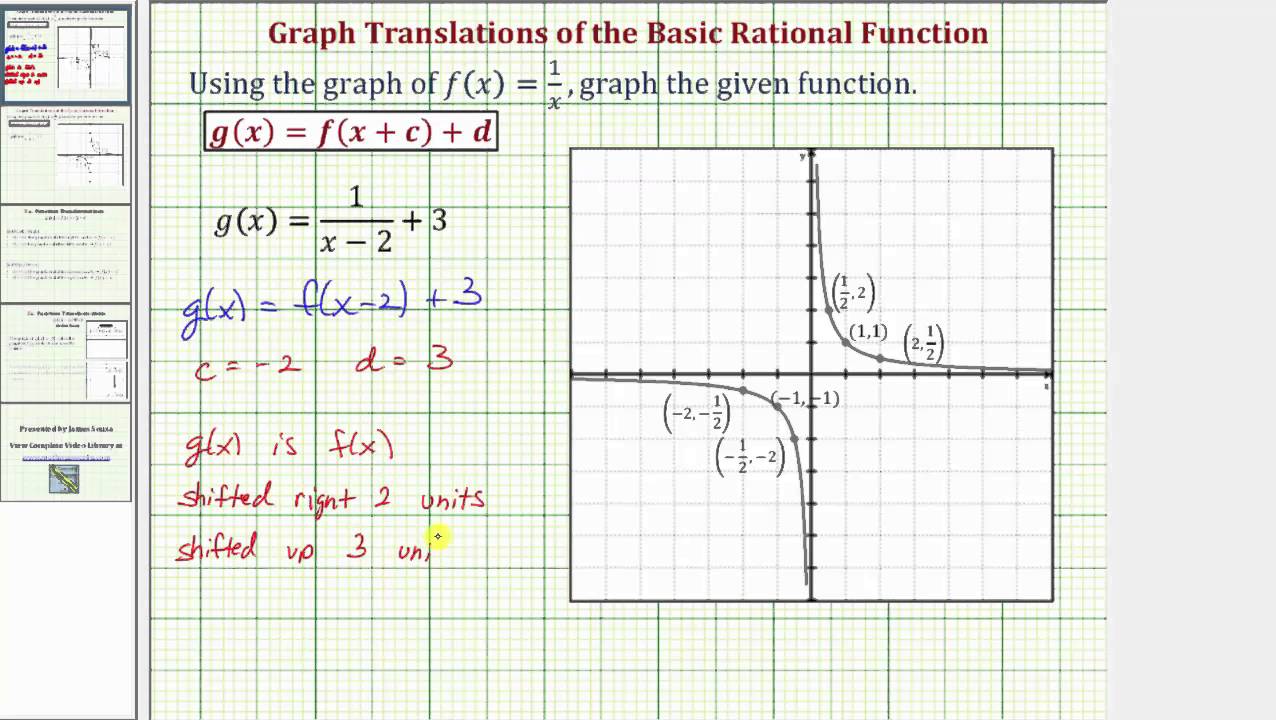



Ex 1 Graph Two Translations Of The Basic Rational Function F X 1 X Youtube
• (b) The expression for the Lagrange remainder is Rn(x) = 1 (n1)!Or e x can be defined as f x (1), where f x R → B is the solution to the differential equation df x / dt (t) = x f x (t), with initial condition f x (0) = 1;Suppose you are given the two functions f (x) = 2x 3 and g(x) = –x 2 5Composition means that you can plug g(x) into f (x)This is written as "(f o g)(x)", which is pronounced as "fcomposeg of x"And "( f o g)(x)" means "f (g(x))"That is, you plug something in for x, then you plug that value into g, simplify, and then plug the result into f




Define The Function F X X 1 X 1 2 X 2 And Draw Its Graph Maths Meritnation Com




Find The Domain And Range Of The Real Function Fx 1 1 X 2 Brainly In
asinus edited by asinus #2 3 I think they cancel each other out and the answer is just 10 Looking at it a little more formally I think it means \ (10= (x1)^3\\ \sqrt 3 {10}1=x\\ f (\sqrt 3 {10}1)= (\sqrt 3 {10}11(x 1)(x 2) (x 2)2 After cancellation, we get lim x!2 (x 1)(x 2) (x 2)2 = lim x!2 (x 1) (x 2) Now this is a rational function where the numerator approaches 1 as x!2 and the denominator approaches 0 as x!2 Therefore lim x!2 (x 1) (x 2) does not exist We can analyze this limit a little further, by checking out the left and right hand limits atThe domain of the function f given by f(x) = (x22x1/x2x6) is (A) R 3, 2 (B) R 3,2 R 2,3 (D) R ( 2, 3) Check Answer and So




4 2 Linear Approximations And Differentials Mathematics Libretexts




Misc 3 Find Domain Of F X X2 2x 1 X2 8x 12
If x = 1 This is true if x= 1, therefore for c= 1 ;2, we have f(c) = 0 In the above case, there is only one such c, however in general cmay not be unique Also it may be di cult to determine the value of c, however the theorem can be used to narrow down where the rootsSo, f is oneone function Clearly, f (x) = x2 x1≥ 3 for all x ∈ N So, f (x) does not assume values 1 and 2 ∴ f is not an onto functionSimple and best practice solution for f(x)=x^3(2x^21) equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework
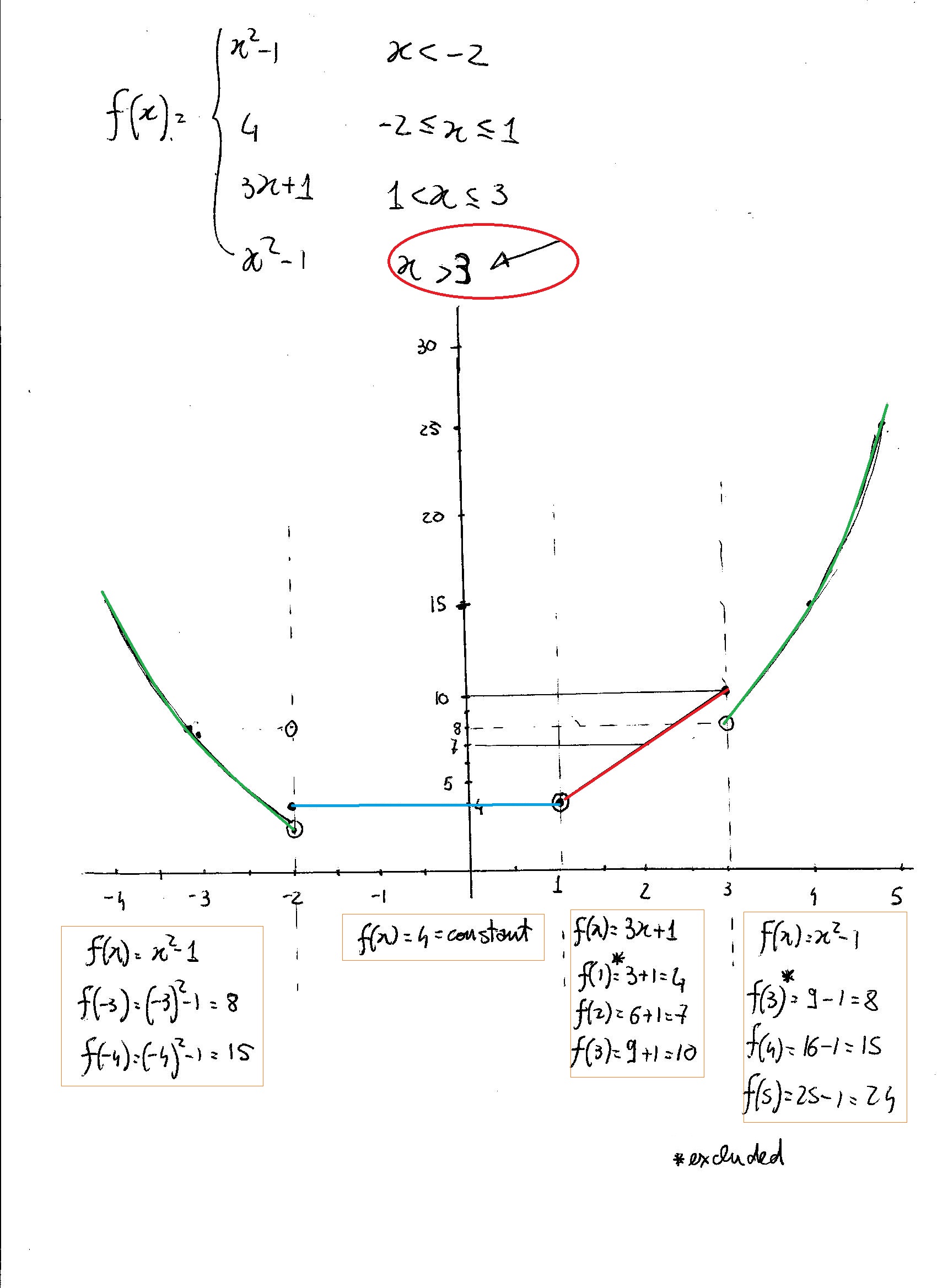



How Would You Graph F X If F X X 2 1 X 2 4 2 X 1 3x 1 1 X 3 X 2 1 X 1 How Would You Evaluate The Function At The Indicated Points F 3 F 2 F 5 F 3 Socratic




If F X Sqrt X 2 1 G X X 1 X 2 1 And H X 2x 3 Then Find F Prime H Prime G Prime X
(i) ω³ = 1, (ii) (1ωω²) = 0 So in order that f(x) be divisible by g(x) , we must have f(ω) = 0 asY = (5x 1)(4 3x); The answer is f^1(x)=(2x1)/(x1) Let y=(x1)/(x2) y(x2)=x1 yx2y=x1 yxx=2y1 x(y1)=2y1 y=(2y1)/(y1) Therefore, f^1(x)=(2x1)/(x1) Verification, f(f^1(x))=f((2x1)/(x1))=((2x1)/(x1)1)/((2x1)/(x1)2) =(2x1x1)/(2x12x2) =3x/3=x graph{(y(x1)/(x2))(yx)=0 10, 10, 5, 5} graph{(y(2x1)/(x1))(yx)=0 10, 10, 5, 5} The graphs are symmetric wrt y=x
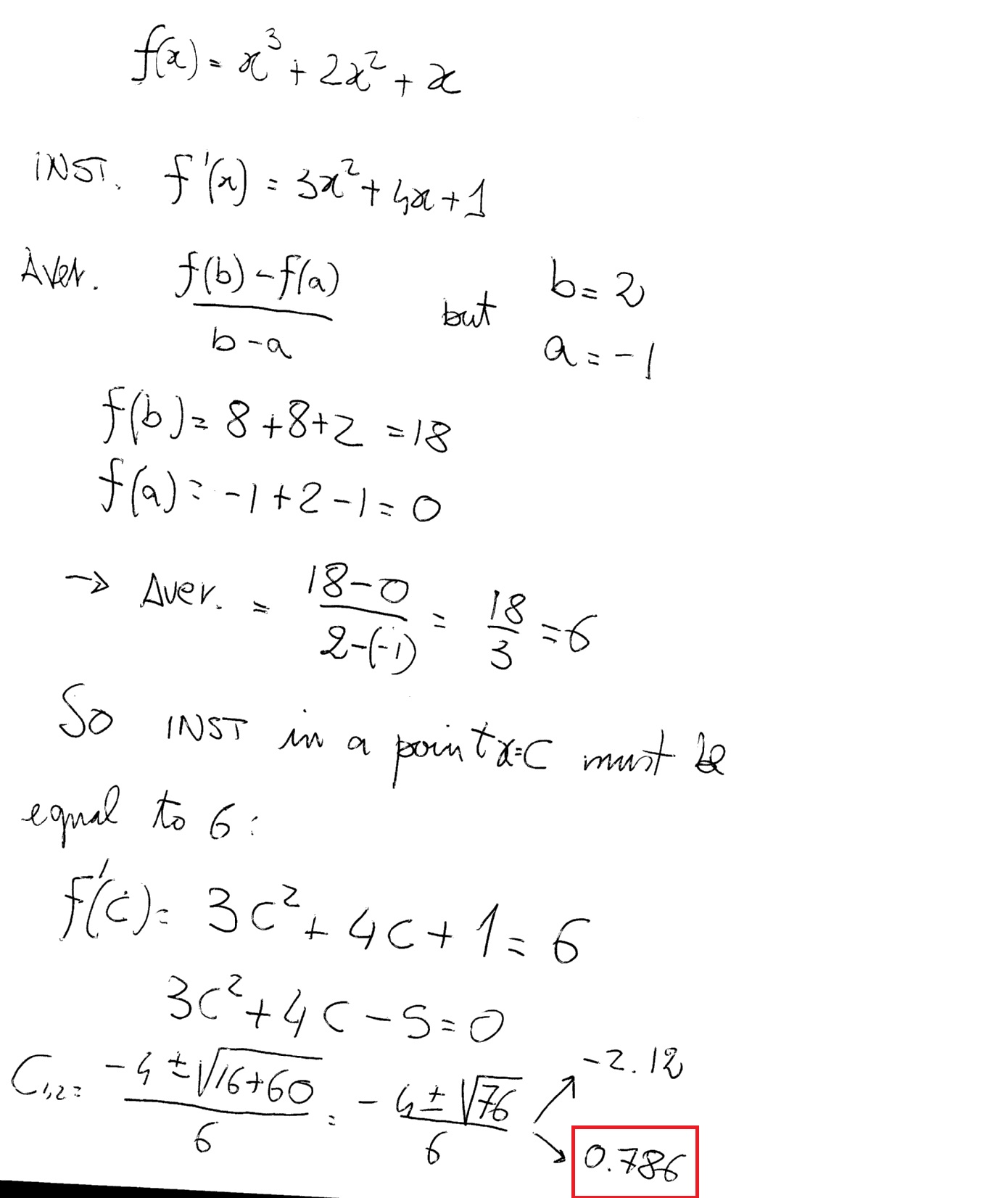



If F Is Defined By F X X 3 2x 2 X How Do You Find The Value Of X When The Average Rate Of Change Of F On The Interval X 1 To X




What Is The Difference Between F X 1 Geq F X 2 And F X 1 F X 2 Mathematics Stack Exchange
X_0 = 1 In Exercises 24 through 27, find all points on the of the given function where the tangent line is f(x) = (x 1)(x^2 8x 7) f(x) = (x 1)(x^2 x 2) f(x) = x^2 x 1/x^2 x 1 InFor x 1, x 2 ∈ R, consider We note that there are point, x1 and x 2 with x 1 ≠ x 2 and f (x 1) = f (x 2), for instance, if we take x 1 = 2 and x 2 = 1/2, then we have f (x 1) =2/5 and f(x 2) =2/5 but 2 ≠ 1/2 Hence f is not oneone Also, f is not onto for if so then for 1∈R ∃ x ∈ R such that f (x) = 1 which gives x/(x 2 1) =1 But there is no such x in the domain R, since theSummary "Function Composition" is applying one function to the results of another (g º f) (x) = g (f (x)), first apply f (), then apply g () We must also respect the domain of the first function Some functions can be decomposed into two (or more) simpler functions




If F X X 1 X 2 X 3 Then A Maximum Value Of F X Is 3 If X In 2 3 B Maximum Youtube
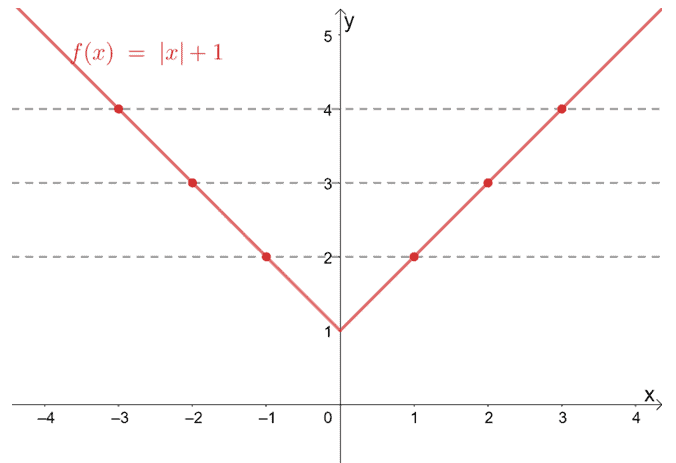



One To One Function Explanation Examples
F(n1)(ξ)xn1 = 1 (n1)!Solution Steps f ( x ) = x ( 2 x ^ { 2 } 1 ) ^ { 2 } ( 4 x ^ { 3 } ) f ( x) = x ( 2 x 2 − 1) 2 ( 4 x 3) To multiply powers of the same base, add their exponents Add 1 and 3 to get 4 To multiply powers of the same base, add their exponents Add 1 and 3 to get 4 x^ {4}\left (2x^ {2}1\right)^ {2}\times 4Graph f(x)=(x1)^22 Find the properties of the given parabola Tap for more steps Use the vertex form, , to determine the values of , , and Since the value of is positive, the parabola opens up Opens Up Find the vertex Find , the distance from the vertex to the focus Tap for more steps
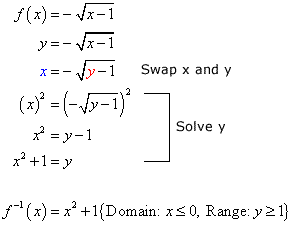



Inverse Of Square Root Function Chilimath




If The Function F X X 2 1 X 1 When X 1 K When X 1
//googl/JQ8NysAdvanced Calculus Uniform Continuity Proof f(x) = x/(x 1) on 2, infinity)F(x) = X∞ k=1 k2xk = x4x2 9x3 ··Ratio Test a k1 a k = (k 1)2xk1 k2xk = (k 1)2 k2 x → x as k → ∞ Thus the series converges absolutely when x < 1 and diverges when x > 1 Radius of Convergence Ratio Test (II) The radius of convergence of a power series can usually be found by applying the ratio test In some casesThe function fR>Rf (x)= (x1) (x2) (x3) check if it is one one ,onto or bijection The function fR>R f (x)= (x1) (x2) (x3) check if it is one one ,onto or bijection ujjeshaa, 5




F X F 1 X 2 Then F 1 2 Is
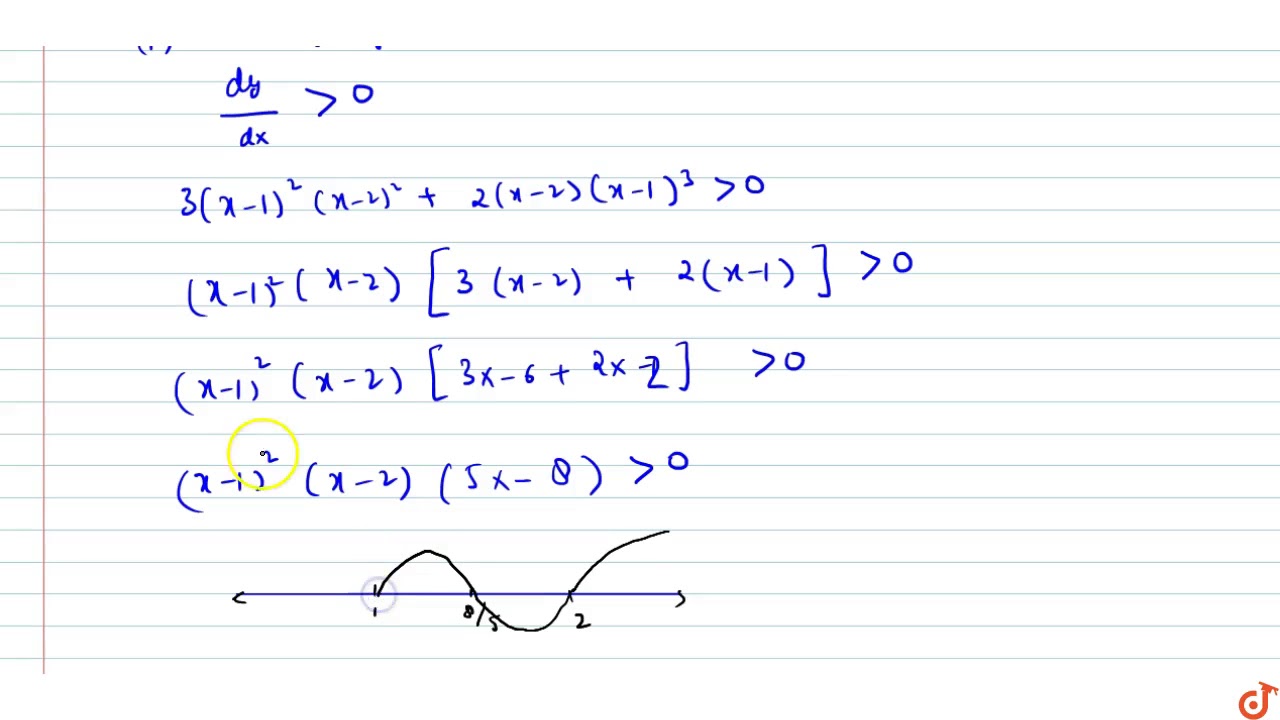



Find The Intervals In Which F X X 1 3 X 2 2 Is Increasing Or Decreasing Youtube




Ex 1 3 6 Show F X X X 2 Is One One Find Inverse Of F




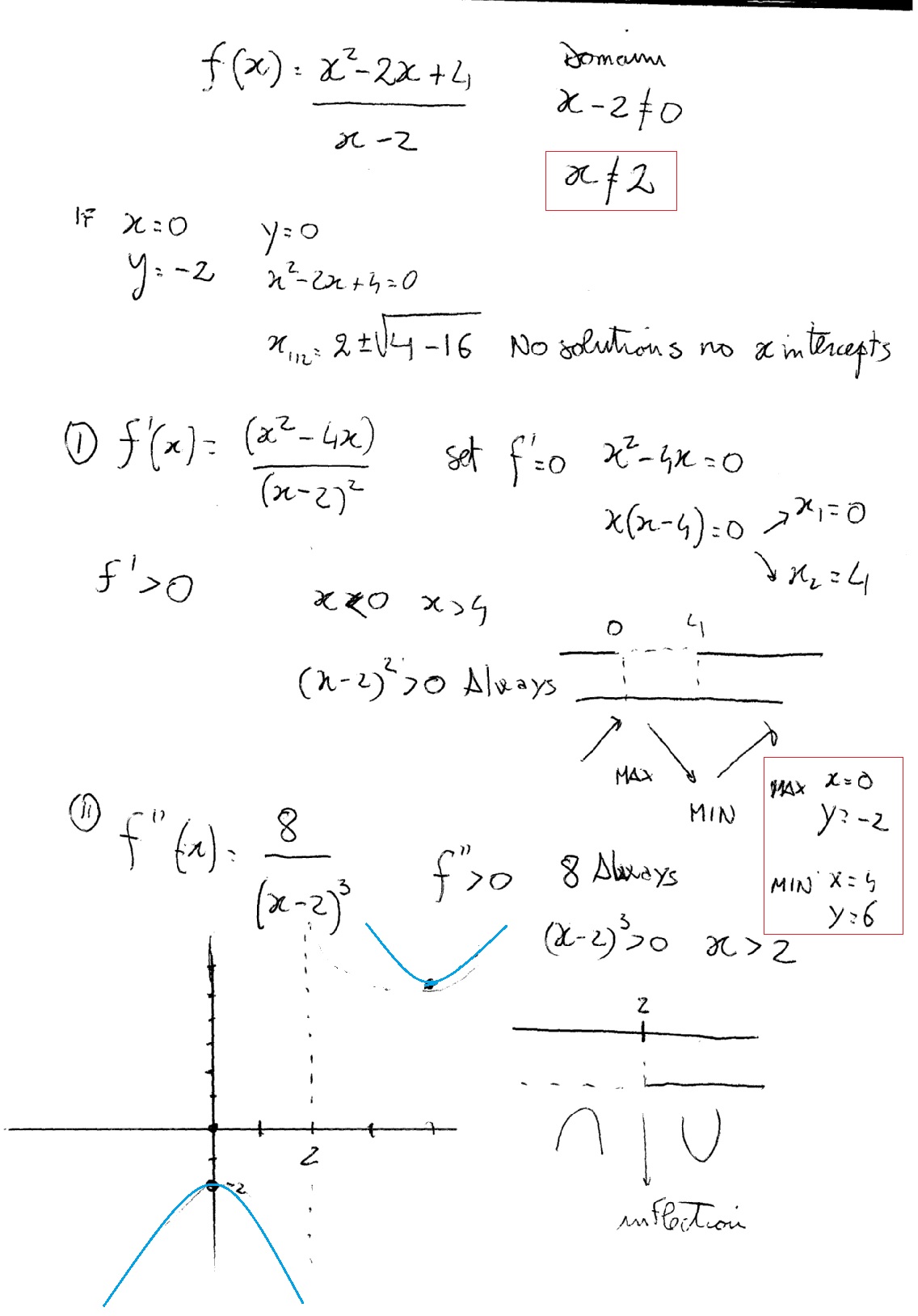
F X X 2 2x 4 X 2 F X X 2 4x X 2 2 F X 8 X 2 3 How To Find The Domain Of F X X And Y Intercepts Vertical Asymptotes The Critical Numbers Concave Up And Down And Sketch Graph Socratic




If F X 2f 1 X X 2 2 X R Then F X Is Given By




Ex 1 3 6 Show F X X X 2 Is One One Find Inverse Of F



If F X X 2 3x 1 How Do You Find X Such That F 2x F X Quora




The Function Y F X Such That F X 1 X X 2 1 X 2
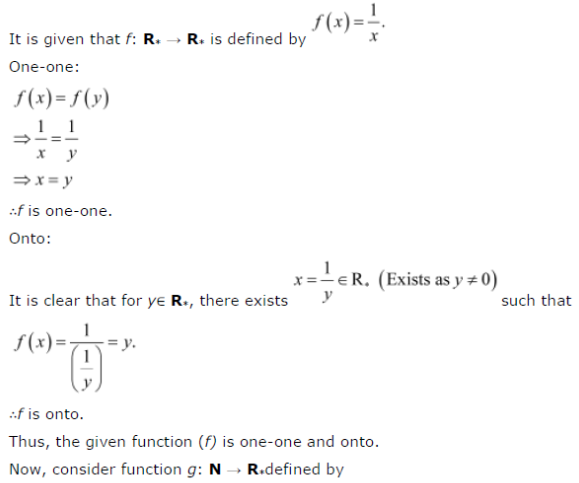



Show That The Function F R R Defined By F X 1 X Is One One And Onto Where R Is The Set Of All Non Zero Real Numbers Cbse Class 12 Maths



Secure Media Collegeboard Org Digitalservices Pdf Ap Apcentral Ap15 Calculus Ab Q2 Pdf



Solution Hello How Do I Graph F X X 2 1 X 1 What Does Lim X Gt 1 X 2 1 X 1 Equal I Graphed The Function With A Discontinuity At X 1 But I 39 M Not Sure How My Second Questio




Example 14 Find Derivative Of F X 1 X X2 X3 X50




If F X X 1 X 0 0 X 0 X 1 X 0
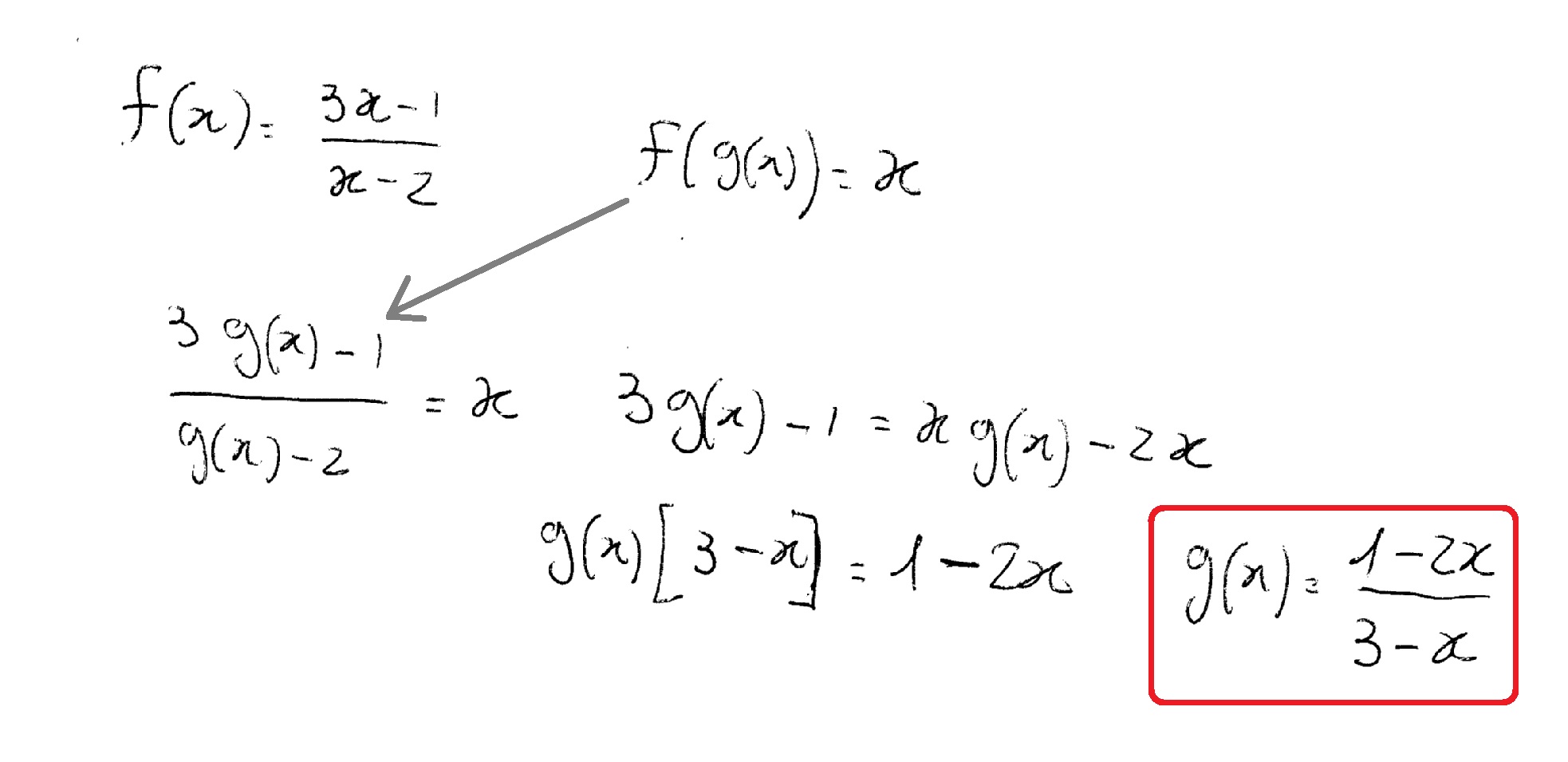



Let F X 3x 1 X 2 And F G X X How Do You Find G X Socratic



Content Newton S Method



Discuss The Continuity Of The Function F X At X 1 2 When F X Is Defined As Follows F X 1 2 X 0 X 1 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



Sage Calculus Tutorial Limits



F X X 2




Show That The Function F R To R Defined By F X X X2 1 For All X Belongs To R Is Neither One One Nor Onto Also If G R To




For The Function Defined By F X X 2 X Less Than Equal To 1 2x 1 X Greater Than 1 Define F 0 And Also Draw The Graph For F X Study Com



Search Q Domain And Range Tbm Isch
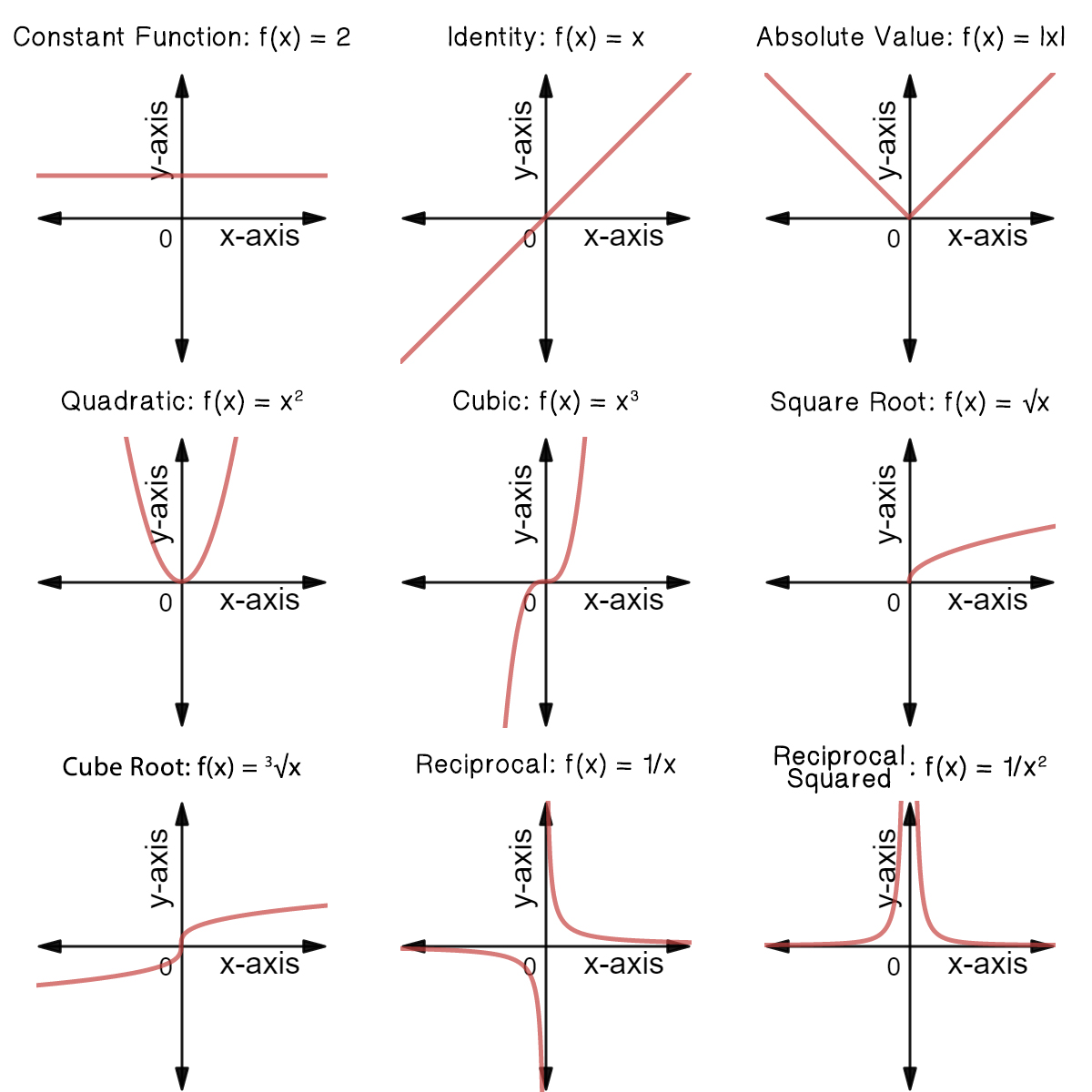



Classifying Common Functions Expii



How To Find Inverse Function Of X 1 X Given That F X Is Bigger Or Equal To 2 Quora




Answered 2 X If X 1 F X X2 1 3d If Bartleby



Curve Sketching



Math Scene Equations Iii Lesson 3 Quadratic Equations




Maximum Value Of Function F X Frac X 4 X 2 X 6 2x 3 1 When X 1 Mathematics Stack Exchange
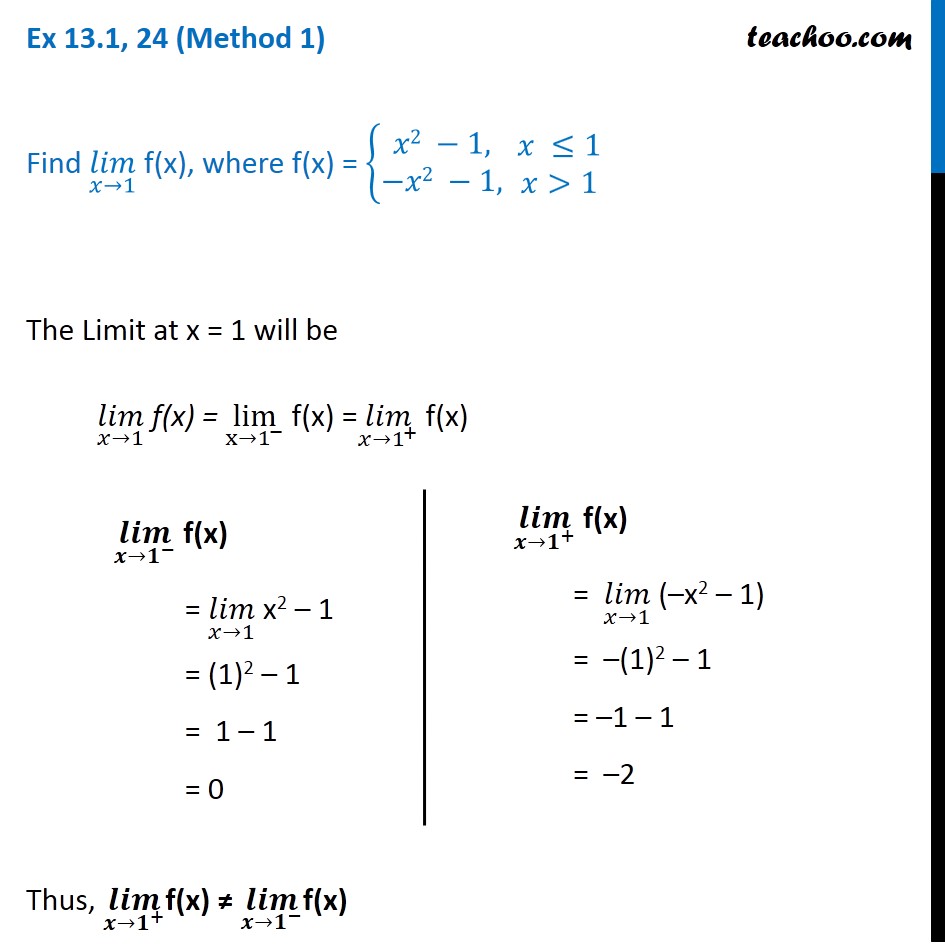



Ex 13 1 24 Find Lim X 1 Where F X X 2 1 X 1 X 2 1



If F X 1 X 1 1 Then F X 1 1 X 1 2 Chegg Com



Www Math Uh Edu Jiwenhe Math1432 Lectures Lecture01 Handout Pdf



F X X Graph




If The Function F R R Defined By F X 4 X4 X 2 Then Show That F 1 X 1 F X And Hence Deduce The Value Of F 14 2f 12 F 34




Use Arrow Notation College Algebra



Find The Derivative Of Arctan 1 X 1 X Stumbling Robot




If F X X 2 1 X 2 Then Find The Value Of F X F 1 X Maths Relations And Functions Meritnation Com



Www Lancasterschools Org Cms Lib Ny Centricity Domain 246 Midyear review answer key Pdf



Www Southalabama Edu Mathstat Personal Pages Jbarnard Archive Teaching Sm13 125 Test1sol Pdf




Solving Polynomial Equations Answers



Consider F X X 2 X 0 X 1 For X 1 For X 1 Chegg Com



Parent Functions




Transformations Of The 1 X Function Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
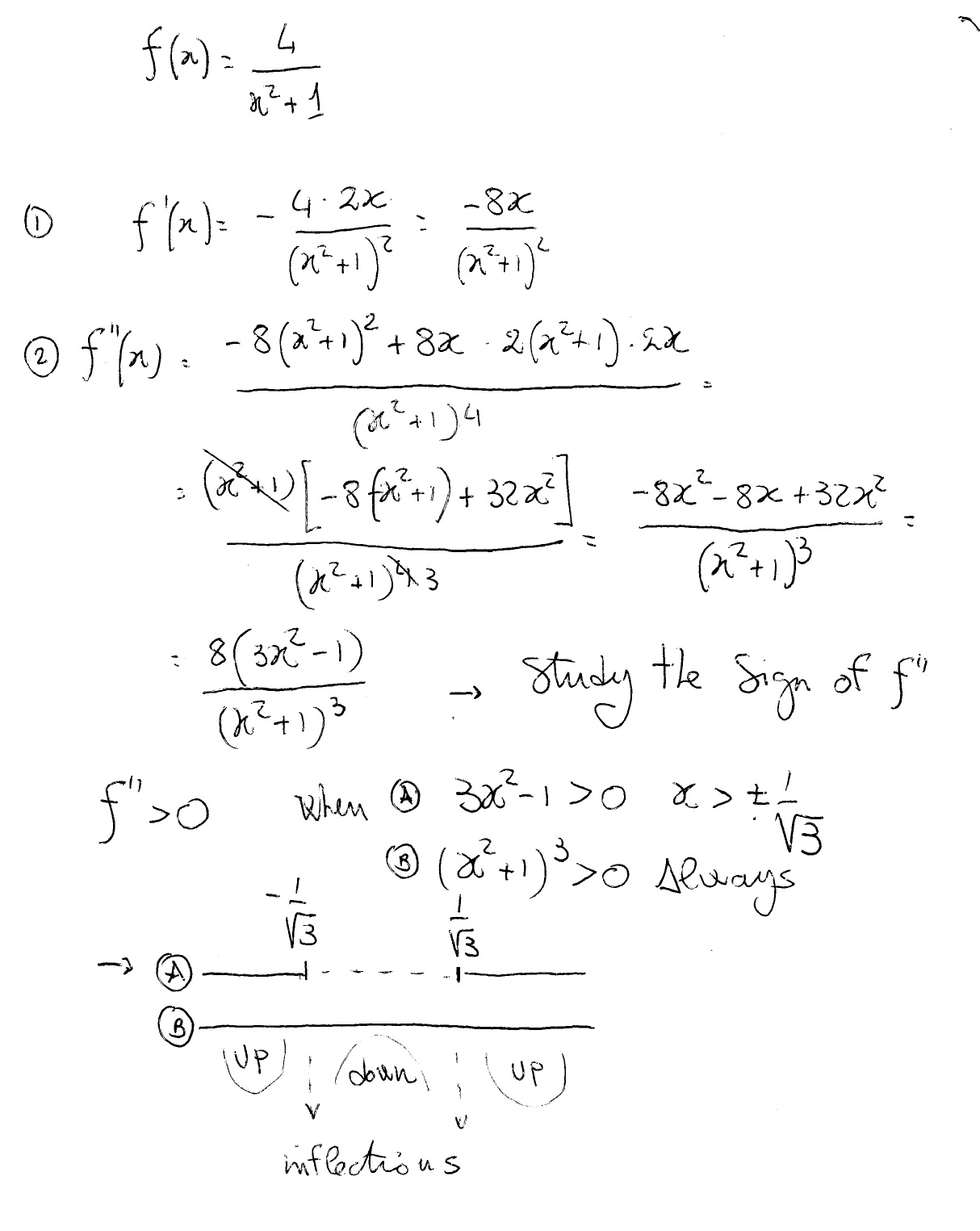



How To Find If A Function F X 4 X 2 1 Is Concave Up Or Concave Down Socratic




Verifying Inverse Functions By Composition Not Inverse Video Khan Academy
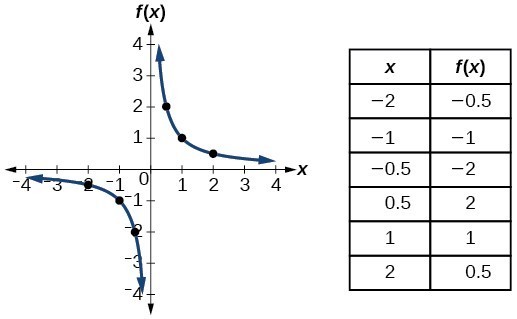



11 1 Toolkit Functions Hunter College Math101



0 1 X




Ex 6 2 11 Prove F X X2 X 1 Is Neither Strictly Increasing



F X X2 2 If 0 X 1 At X 1 2x2 3x 3 2 If 1 X 2 Studyrankersonline




If F X X 1x 1 Then F 2x In Terms Of F X Is



Operations On Functions Translations Sparknotes




X2 X 1 X2 X 1 Find The Range Of F X Scholr




Is Function Of F X X 2 1 X 1 Continuous At X 1 Quora
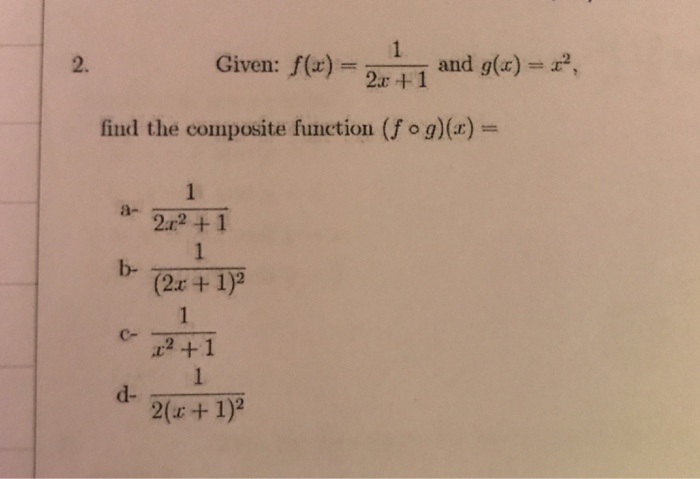



Given F X 1 2x 1 And G X X 2 Find The Chegg Com
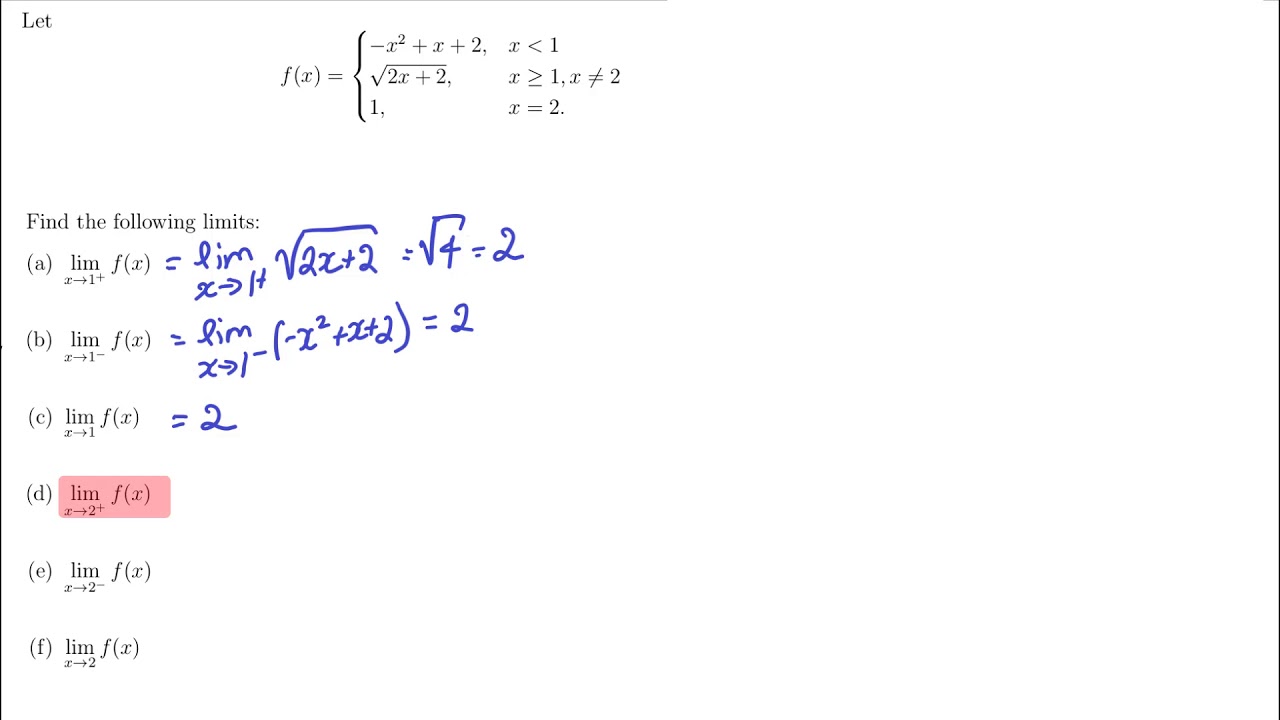



Computing Limits Algebraically



Www Ualberta Ca Rjia Math215 Hwks Sol8 Pdf
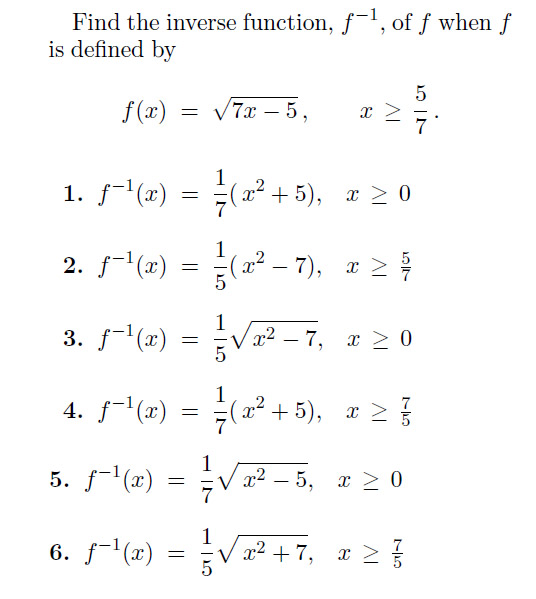



Find The Inverse Function F 1 Of F When F Is Chegg Com




Interpret The Graph Of Frac Ax B Cx D As A Transformation Of Y Frac 1 X Mathematics Stack Exchange



Let F X 1 X 0 X 2 F X 3 X 2 X 3 Determine The Form Of G X F F X And Hence Find




Taylor Series Wikipedia
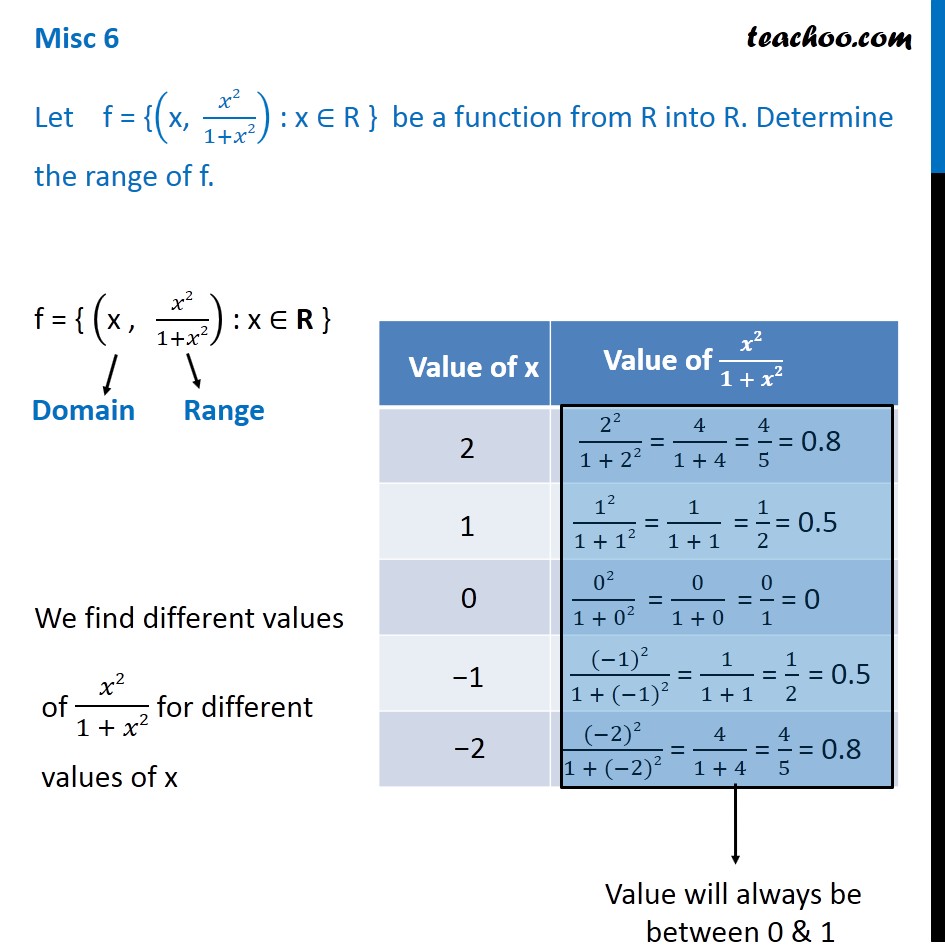



Misc 6 Let F X X2 1 X2 X R Find Range Chapter 2
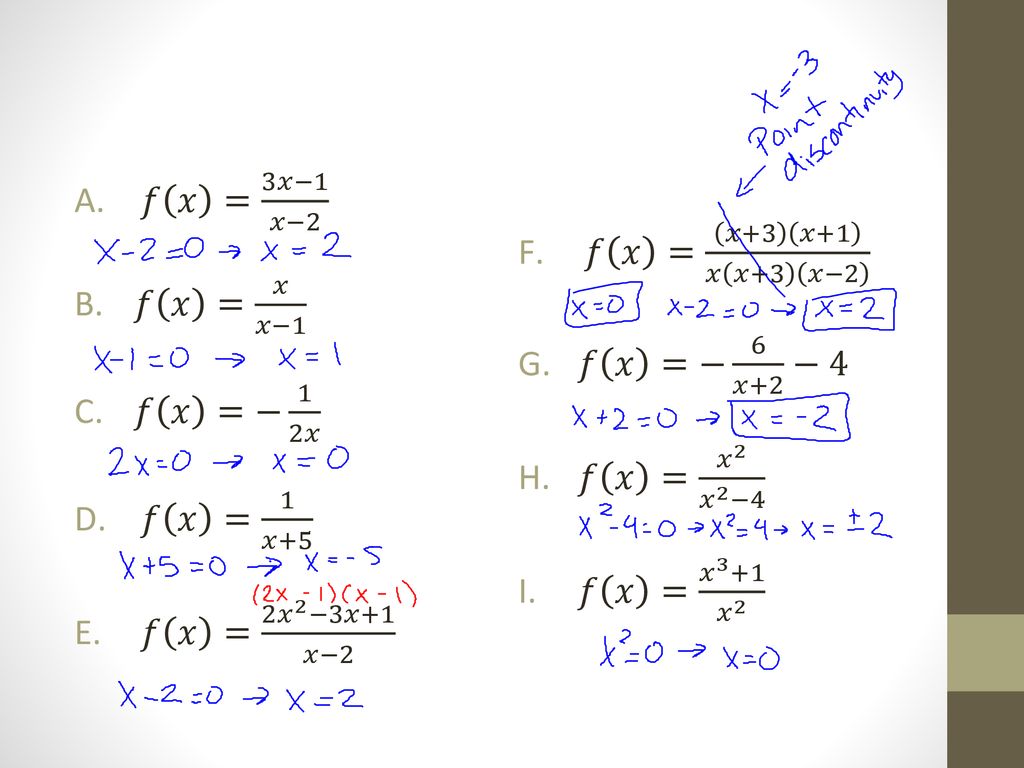



3 7 Graph Of Rational Functions Ppt Download



Answer In Algebra For Dani Wagas




Find The Derivative Of The Function Given By F X 1 X 1 X2 1 X4 1 X8 And Hence Find F 1 Mathematics Shaalaa Com




Finding Inverse Functions Quadratic Example 2 Video Khan Academy




Find The Domain And Range Of The Function F X 1 1 X 2 X In R X 1 Dot



Math Scene Equations Iii Lesson 3 Quadratic Equations




Composite Functions When Two Or More Functions Are Combined So That The Output From The First Function Becomes The Input To The Second Function The Result Ppt Download




Graph A Rational Function



When Is The Limit Of F X Undefined



Find The Value Of A If The Function F X Defined By F X 2x 1 X 2 And A X 2 And X 1 X 2 Is




Range Of The Function F X X X 2 X X 1 Where X Is A Real Number Is Askiitians




Find The Derivative Of F X Squareroot X 1 X A Chegg Com



Examine The Differentiability Of F Where F Is Defined By F X 1 X If X 2 5 X If X 2 At X 2 Studyrankersonline


